Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS)
An adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) integrates neural networks and fuzzy logic, first introduced by Jyh-Shing Roger Jang in 1993. It combines the interpretability of fuzzy inference systems with the adaptive learning ability of neural networks to build a mapping between inputs and outputs using fuzzy rules and network training. ANFIS excels at handling uncertainty and nonlinear problems by modeling complex relationships between inputs and outputs.
Principles of ANFIS
Fuzzy Inference System (FIS)
A fuzzy inference system (FIS) forms the core of ANFIS, using fuzzy logic to mimic human decision-making. Typical FIS steps include:
- Fuzzification: convert precise inputs into fuzzy sets via membership functions (e.g., Gaussian).
- Fuzzy rules: define fuzzy relationships between inputs and outputs.
- Fuzzy inference: derive fuzzy outputs based on the rules.
- Defuzzification: convert fuzzy outputs back into precise values.
FIS handles fuzzy data well but relies on manually set parameters, lacking self-adaptation.
Neural Networks
Neural networks learn data-driven relationships between inputs and outputs through layered neurons and weight updates, effectively extracting patterns but with limited interpretability.
Integrating ANFIS
ANFIS represents fuzzy inference as a neural network, leveraging the learning ability to fine-tune fuzzy rules’ parameters:
- Both membership function (premise) parameters and rule output (consequent) parameters are trainable.
- A hybrid approach (backpropagation + least squares) automatically adjusts parameters to fit the data.
This integrates fuzzy logic’s interpretability with neural networks’ adaptability.
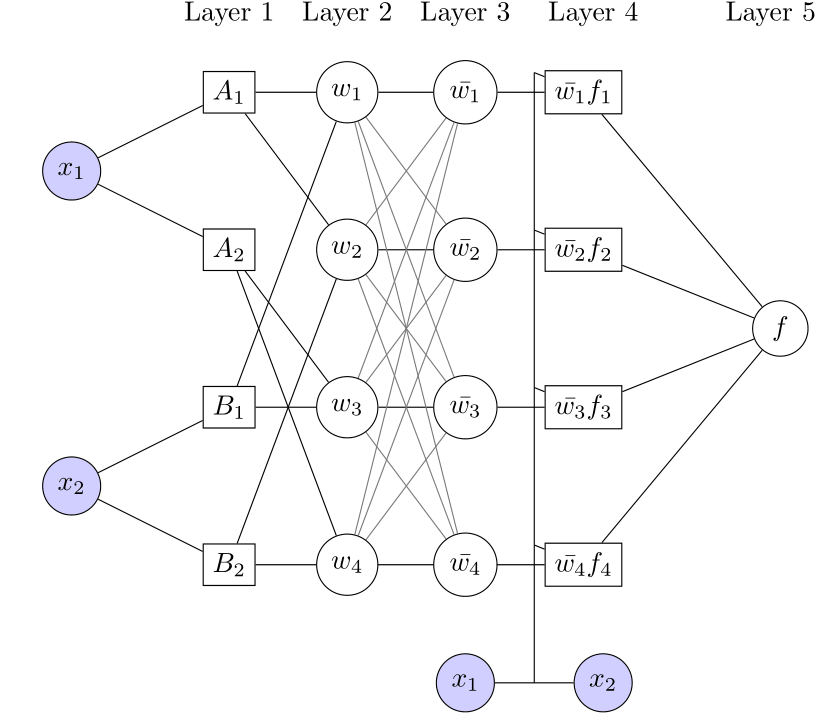
ANFIS Structure
ANFIS has five layers, each corresponding to a step in the fuzzy inference system:
- Fuzzification Layer (Layer 1)
- Performs fuzzification on inputs.
- Math: For input $x$, output is $O_{1,i} = \mu_{A_i}(x)$.
- Rule Layer (Layer 2)
- Computes each fuzzy rule’s firing strength.
- Math: $w_i = \mu_{A_i}(x) \cdot \mu_{B_i}(y)$.
- Normalization Layer (Layer 3)
- Normalizes firing strengths.
- Math: $\bar{w}_i = w_i / \sum w_j$.
- Defuzzification Layer (Layer 4)
- Computes each rule’s output, usually with a linear function.
- Math: $\bar{w}_i f_i = \bar{w}_i (p_i x + q_i y + r_i)$.
- Total Output Layer (Layer 5)
- Aggregates outputs from all rules.
- Math: $f = \sum \bar{w}_i f_i$.
Training ANFIS
ANFIS trains in two stages using a hybrid algorithm:
- Forward pass: holds premise parameters fixed and uses least squares to solve for consequent parameters.
- Backward pass: holds consequent parameters fixed and uses gradient descent for premise parameters.
This balances efficiency and accuracy.
ANFIS Applications
ANFIS is used in areas like control, signal processing, time series prediction, and classification:
- Automatic control: robot control, air-conditioning adjustments.
- Signal processing: speech recognition, noise filtering.
- Time series prediction: weather, stocks.
- Classification and diagnosis: medical diagnosis, fault detection.
In autonomous driving, for example, ANFIS can smooth braking based on fuzzy inputs (e.g., “short distance,” “high speed”).
Implementing ANFIS in Python
Example of fitting a sine function with the anfis library:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
import numpy as np
import anfis
from anfis import membership
from anfis import mfDerivs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Generate training data
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
# Define membership functions
mf = [[['gaussmf', {'mean': 0., 'sigma': 1.}],
['gaussmf', {'mean': 5., 'sigma': 1.}],
['gaussmf', {'mean': 10., 'sigma': 1.}]]]
# Create ANFIS model
model = anfis.ANFIS(n_inputs=1, n_rules=3, mf=mf)
# Train the model
model.trainHybridJangOffLine(epochs=10, X=x.reshape(-1, 1), Y=y.reshape(-1, 1))
# Predict
y_pred = model.predict(x.reshape(-1, 1))
# Plot results
plt.plot(x, y, 'b-', label='True')
plt.plot(x, y_pred, 'r--', label='Predicted')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('ANFIS Fitting Sine Function')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
Code Notes
- Data: $x$ as input, $y = \sin(x)$ as target.
- Membership functions: three Gaussians centered at 0, 5, and 10.
- Training: hybrid algorithm for 10 epochs.
- Result: visualization of actual vs. predicted outputs.
Pros and Limitations
Pros
- Handles uncertain/imprecise data.
- Hybrid advantage of fuzzy logic + neural networks.
- Automatically adjusts parameters.
Limitations
- Requires sufficient data.
- Risk of overfitting with complex models.
- Computational cost grows with higher dimensions.
- Single-output limitation.
ANFIS-Related Work
- S-ANFIS: S-ANFIS is a straightforward extension of the ANFIS network, where inputs for the premise and consequent parts can be controlled separately.
Conclusion
ANFIS combines neural network adaptability with fuzzy logic’s interpretability, suitable for nonlinear and uncertain tasks. Since its inception, ANFIS has been widely adopted in control and signal processing. The anfis Python library makes it straightforward to build and apply ANFIS models to various problems.